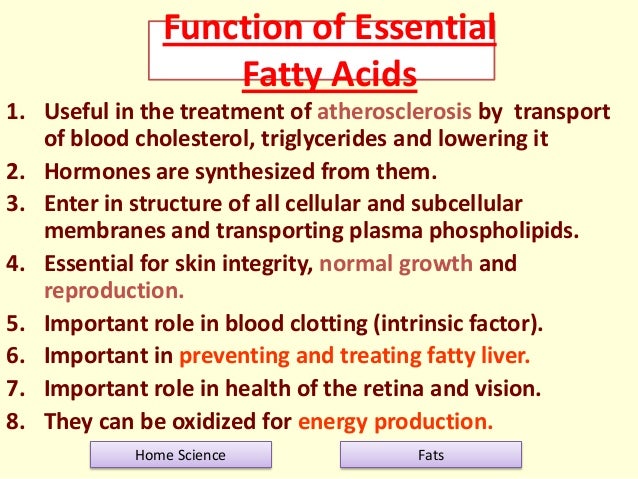
Fats are essential to good health and you need to consume some every day for your body processes to work efficiently. Fat is a necessary nutrient for using fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) and a dense energy source. Additionally, the fat in the diet helps with growth, brain and nervous system

Monounsaturated Fat vs. Polyunsaturated Fat. These two types of unsaturated fats have some things in common but are both individually important in their own right.
Dietary fat has a bad reputation, but fat isn’t necessarily a bad thing. Learn how saturated vs. unsaturated fats stack up and what this means for you.
Types of fats in food; Unsaturated fat. Monounsaturated fat. ω−7; ω−9; Polyunsaturated fat. ω−3; ω−6; Trans fat; Saturated fat. Interesterified fat; See





For years, fat was a four-letter word. We were urged to banish it from our diets whenever possible. We switched to low-fat foods. But the shift didn’t make…

Unsaturated fat comes in two forms: monounsaturated and polyunsaturated. Including these healthy fats as a part of a well-balanced diet can result in a

Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP): ATP is a molecule that serves as the universal energy source for all plants and s. In your body, ATP breaks down into adenosine diphosphate plus a separate phosphate group. This releases energy, which is used to power your body’s cells.
What are polyunsaturated fats? From a chemical standpoint, polyunsaturated fats are simply fat molecules that have more than one unsaturated carbon bond in the molecule, this is also called a double bond.
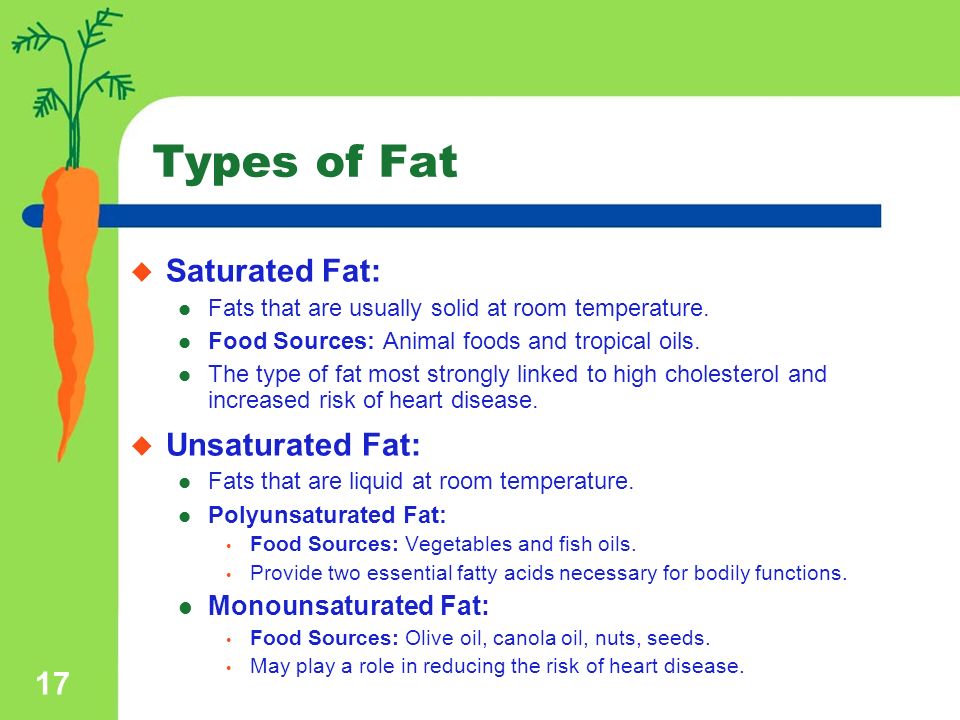
A saturated fat is a type of fat in which the fatty acid chains have all or predominantly single bonds.A fat is made of two kinds of smaller molecules: glycerol and fatty acids.Fats are made of long chains of carbon (C) atoms. Some carbon atoms are linked by single bonds (-C-C-) and others are linked by double bonds (-C=C-). Double bonds …
Fat’s not the enemy, if you’re smart about it. Eat these 17 high-fat foods that are full of mostly healthy fats.